The ability to hear is a fundamental facet of a kid’s turn of events, playing a vital job in their ability to learn the language, communicate, and socialize. Regular children’s hearing test known as pediatric audiometry, guarantee the early location of any potential hearing impairment.
Pediatric hearing tests are planned specifically to evaluate the hearing ability of youngsters. It incorporates babies, infants, little children, and more seasoned youngsters. The techniques utilized are painless and completely safe. A hearing test may be suggested by a pediatrician if there are worries about the youngster’s hearing or as part of a regular examination to guarantee a normal turn of events.
How Does a Pediatric Hearing Test Work?
The procedure of children’s hearing test varies relying on the kid’s age, developmental stage, and ability to cooperate.
The OAE test measures sound created by the internal ear because of a soft clicking noise presented via a little test placed in the baby’s ear. If the internal ear does not transmit a sound accordingly, it could indicate a hearing misfortune.
The ABR test, then again, measures the electrical activity of the auditory nerve utilizing adhesive cathodes placed on the baby’s head. A reliable test can recognize even gentle types of hearing misfortune.
For babies and more established kids who can answer directions, the Unadulterated Tone Audiometry Test is utilized. In this test, kids wear headphones and answer when they hear sounds at various frequencies and volumes, often by raising their hands or squeezing a button.
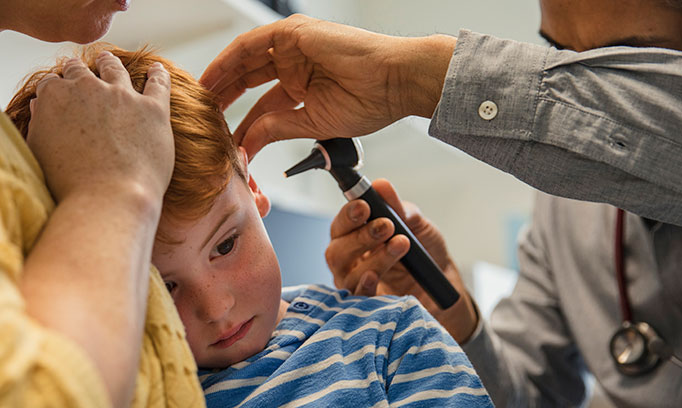
Is a Pediatric Hearing Test Safe?
All these tests are safe, painless, and harmless. No radiation is utilized, and the procedures don’t cause discomfort. Often, they can be finished while the kid is resting, especially for babies and infants. For more established youngsters, the tests are intended to be engaging and fun, making the kid comfortable during the procedure.
Importance of Pediatric Hearing Tests
Early identification of hearing misfortune is crucial in kids. It enables early mediation, which significantly works on the results for the kid’s language advancement, academic performance, and social abilities.
Undetected hearing misfortune can lead to delays in discourse and language advancement, affecting the youngster’s social interactions and academic advancement.
















